Advertiser Disclosure
All About Cookies is an independent, advertising-supported website. Some of the offers that appear on this site are from third-party advertisers from which All About Cookies receives compensation. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site (including, for example, the order in which they appear).
All About Cookies does not include all financial or credit offers that might be available to consumers nor do we include all companies or all available products. Information is accurate as of the publishing date and has not been provided or endorsed by the advertiser.
Editorial Policy
The All About Cookies editorial team strives to provide accurate, in-depth information and reviews to help you, our reader, make online privacy decisions with confidence. Here's what you can expect from us:
- All About Cookies makes money when you click the links on our site to some of the products and offers that we mention. These partnerships do not influence our opinions or recommendations. Read more about how we make money.
- Partners are not able to review or request changes to our content except for compliance reasons.
- We aim to make sure everything on our site is up-to-date and accurate as of the publishing date, but we cannot guarantee we haven't missed something. It's your responsibility to double-check all information before making any decision. If you spot something that looks wrong, please let us know.
Smishing (a combination of the words SMS and phishing) is a socially engineered scam where cybercriminals use fraudulent text messages to manipulate people into sharing private information. Then cybercriminals can use that information to steal money.
And it's a popular tactic. Americans received 10.89 billion spam texts in August 2022 alone. Even the IRS recently warned of a rise in texting scams impersonating the IRS.
Unlike email, your mobile phones don't have strong filters to block text messages containing spam or smishing attempts. That's why cybercriminals like to target individuals via texts; it's easier to get fake texts delivered to you compared to phishing emails.
Keep reading to learn more about how smishing works, examples of what cybercriminals say in smishing messages, and what you can do to prevent smishing scams.
Phishing vs. smishing
What is vishing?
7 most common smishing scams
1. Fake order/account confirmation messages
2. Urgent messages from financial services
3. Customer support impersonation
4. Bogus gift and giveaway notifications
5. Malware attacks
6. Spear smishing
7. COVID-19 scams
How to mitigate smishing scam effects
Smishing warning signs and prevention
Smishing FAQs
Bottom line
How does smishing work?
Smishing is conducted over SMS messages, but the initial text will vary. Most of the time the cybercriminal will pose as a trusted person or business. They may even use spoofed phone numbers or inaccurate caller IDs to mislead you about the source.
Smishing will usually include a link, so the malicious text message will use social engineering tactics to convince you to click on it. Social engineering is a method to manipulate victims into trusting the sender usually by impersonating a trusted person or organization.
When you click on a malicious link you may either have malware downloaded on your mobile device or be redirected to a fake website asking for your password, two-factor authentication code, banking information, or other personal data.
Phishing vs. smishing
Smishing is a type of phishing attack. Both tactics involve manipulating people to fall into a trap or get involved in a scam. The main difference between phishing and smishing is where it happens. Smishing specifically focuses on SMS text messages while phishing can happen anywhere online — like emails or direct messages on social media.
What is vishing?
Vishing is another form of phishing. This version of phishing happens over a phone call. Similar to smishing, it uses social engineering tactics, like impersonating a trusted source and creating an urgent situation, to convince you into sharing sensitive information like credit card information or Social Security numbers.
7 most common smishing scams
There are several types of smishing scams, but they all share common characteristics. Here's a quick overview of the most common smishing scams and some examples.
1. Fake order/account confirmation messages
Attackers will pose as a business and send you a message claiming a shipment is being sent to you. In other cases, they may say you need to confirm your account.
Take a look at this real smishing scam example. The cybercriminal used a spoofed phone number and sent a message claiming a package was sent. The link is also suspicious since it's not clear who the sender is based on the URL.

Some further research confirms this is a smishing attempt. The link contains duckdns.org, which is an authentic website but it is often used by cybercriminals as part of a phishing campaign.
2. Urgent messages from financial services
Getting access to your financial information is extremely valuable to hackers. But it's also a bit tricky to hack. They will need your account login credentials and possibly a two-factor authentication code to gain access. One of the ways they accomplish this is by sending you a message that is claiming there is an urgent situation.
For example, take a look at this real smishing text. The sender poses as a credit union with a spoofed phone number and claims a hold has been placed on an account. It also sends an unsolicited link to resolve the issue.
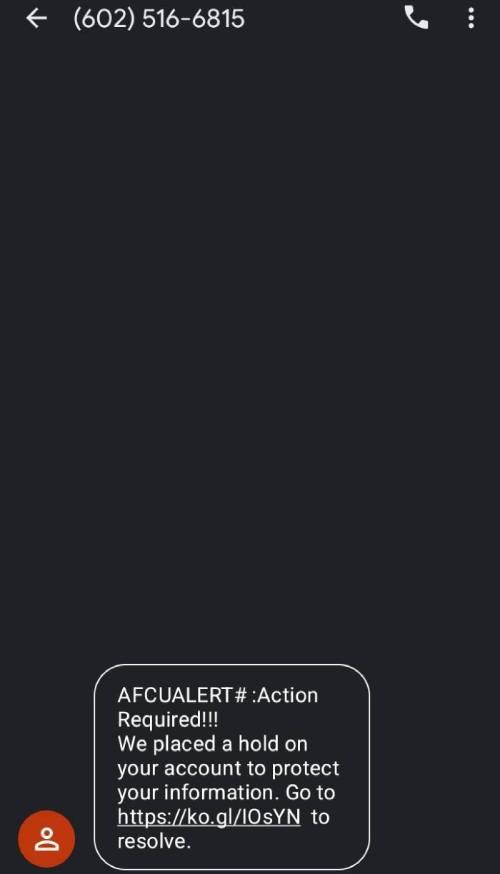
Since having your bank account placed on hold can cause you to feel panicked, you may quickly click on the link and fill out the requested information without thinking twice about it. But this is a smishing attempt since this specific financial institution doesn't send unsolicited links.
3. Customer support impersonation
Another scenario is for attackers to pretend to be customer support. They'll pick a company you most likely use (like Amazon or PayPal) and then send you a fake text message to verify expensive purchases.
Obviously, you didn't make those purchases, so you respond to say you didn't authorize the transaction. Then the conversation turns into resetting your password, and the fraudster does it in a way where you have handed over sensitive data, like your credit card information.
4. Bogus gift and giveaway notifications
The initial smishing text tells you that you've won a giveaway or prize. While this sounds like great news, this is usually a lure to get you to respond. There are actually cybercriminals behind the supposed free gifts, and they will ask you to claim your prize by paying a small fee. Other times they'll send you a link to fill out a form designed to steal your sensitive information.
5. Malware attacks
Sometimes the goal of a smishing attack isn't necessarily to steal your information — at least at first. Attackers may want you to accidentally install malware onto your phone. They accomplish this by convincing you to click on a malicious link in a text message. Once your mobile device has downloaded the malware, cybercriminals can start tracking your behavior, steal personal information, or cause harm to your device.
6. Spear smishing
Spear smishing is a more targeted version of phishing. It targets specific people or organizations over text messages. A common example of this is CEO fraud. An attacker will impersonate a CEO or another high-ranking manager and then send fake requests to employees.
The impersonated CEO may text employees asking for them to buy gift cards with their own money, which will be reimbursed by the company later. Since you may want to please your boss, you might fulfill the fraudulent request without noticing the red flags of a scam.
7. COVID-19 scams
Cybercriminals took advantage of the panic related to the pandemic by sending COVID-19 scams. They used smishing to send spam texts claiming people had been exposed. Then, they were directed to fake websites to buy masks and hand sanitizer.
How to mitigate smishing scam effects
So what happens when you receive a smishing scam? The best thing to do is to not interact with the text message. If you don't respond or open any links, then there is no harm being done to you. But if you have already responded to the smishing scam, there are some ways to fix the situation.
Here are some steps to consider if you are a victim of a smishing scam:
- Forward the scam text to 7726 (SPAM) for investigations by mobile carriers.
- Contact the organization directly with a known number to report suspicious texts.
- Report suspicious text messages to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) or the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
- If you've given out your password, change it immediately. If you used the same password for other online accounts, you'll also need to change it there too. Password managers can help you store them securely.
- Check your bank accounts and credit cards to ensure transactions are authentic. Report anything unauthorized.
Smishing warning signs and prevention
Smishing scams often share the same red flags. Here are some signs that the text message you received isn't authentic and possibly a scam:
- Sense of urgency: Attackers often want you to feel panicked so you don't stop to think about your decisions. Their text messages will ask you to respond immediately.
- Grammatical errors: Spelling mistakes aren't normal for organizations or businesses. You should be suspicious of errors in grammar from texts claiming to be from well-known brands.
- Suspicious phone numbers: If you don't recognize the phone number, then there's a chance it's a scammer. This is especially true if the text is from a business, and it's not the same phone number that you have previously contacted.
- Asks you to share personal information with them: Usually, attackers won't start the smishing scam by directly asking for your credit card number, but the conversation will eventually ask you to divulge private information.
If you're looking to avoid smishing scams, here are some tips:
- Don't respond to unsolicited text messages or phone numbers you don't recognize.
- Don't send personal or sensitive information over a text message.
- Don't click on any links or respond to the message.
- Check the privacy settings of your mobile device to enable spam protection.
- Don't give out your phone number if you don't need to.
Smishing FAQs
What are some smishing examples?
Smishing examples usually involve a cybercriminal impersonating a trusted person or business. Then they will send text messages claiming you've won a prize, need to update your account information, or owe money to the government.
Smishing is designed to either excite or scare a person into responding. Then the cybercriminal will ask for personal data and use it to steal money or learn more sensitive information about you.
Can you get malware from opening a text?
You usually can't get malware from opening a text. You'll most likely need to click on a malicious link or attachment first to get malware installed on your phone.
While it's unlikely for your phone to download malware from opening a text, researchers have shown a phone can get hacked by receiving a message. Keeping your phone updated is the best way to have the latest security patches to prevent this from happening.
How do I stop smishing texts?
You can stop smishing texts by blocking the phone number. You can also forward the suspicious text to 7726 (SPAM) to alert mobile carriers of potential spam. While it's annoying to receive smishing texts, they are usually not harmful as long as you don't respond or click on any links.
Bottom line
Smishing happens frequently. On average, nearly 39 spam texts for every person in the U.S. were sent in August 2022. You can be proactive by reporting smishing attempts to government authorities or the organization that's being impersonated.
You can also check your phone settings to ensure spam protection is turned on. While you may still occasionally receive smishing attempts, you can minimize your risk of getting scammed by not responding to spam messages.
If you want to ensure you have strong cybersecurity, consider using password managers, signing up for identity theft protection, or taking measures to delete your cell phone number from the internet.
-
Excellent identity theft protection service
-
Includes a password manager and VPN
-
Robust tools for children’s security
-
Provides VantageScore and not FICO score updates





